Imagine how much money your business would lose if you lost half of your site traffic over night, because of a Google Algorithm update you didn’t know about.
Staying informed on Google activity is a sure-fired way to succeed on the search engines. On average, Google updates its algorithm three times each day, that is between 600 and 900 updates every year! But not all updates are created equally, and a majority will not impact your search engine rankings. However, a handful of times per year, an update will arrive that caused more of an impact than the others.
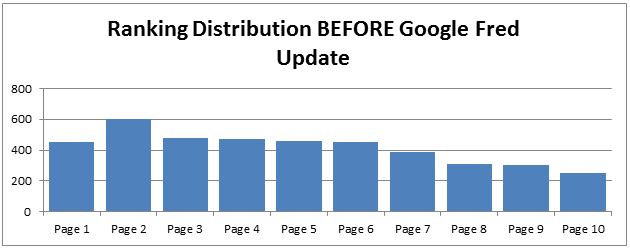
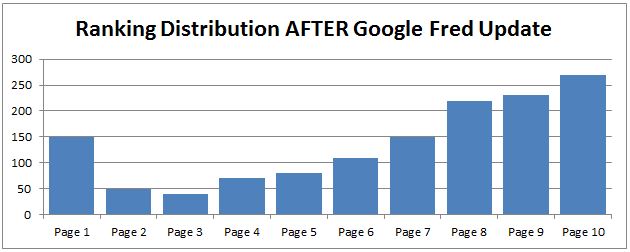
In Q1 2017, a new Google algorithm update called Fred is buzzing around the SEO world lately. In March, many SEOs started speculating that Google was shaking up keyword rankings. After several weeks of an uncertainty, Google employees began to confirm this latest update as Google Fred.
As usual, Google provided no forewarning for this major algorithm shake-up. When Google Fred was confirmed, Google employees stated that this update only furthered Google’s best practices already in place.
SEO reporting platforms were showing a large difference in rankings, good and bad, and a deep impact on organic traffic for these affected sites. A deeper dive discovered that a majority of the sites being affected were using black hat SEO tactics to gain backlinks. Much like the Penguin update, it appears that Fred is trying to remove spam-heavy sites from the SERPs.
So, if your site has lots of external spammy links, thin content, and/or content aimed at ad-revenue techniques, you may have seen a drop in rankings. On the opposite end, a site with high-quality content and links may have moved up in rankings.
How can you tell if your site has the right “high-quality” ingredients for SEO? Today, we’ll give you the steps to take to right your organic keyword ranks by identifying key Google’s best practices.
Tip 1 – Check Your Google Analytics Tag
One big shake-up of Google Fred is the Google Analytics tag update. Some sites whose Analytics data was reporting a significant drop in traffic were not actually seeing a drop at all.
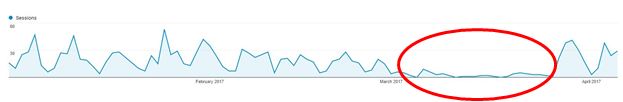
If your Google Analytics is using an outdated Classic Analytics tag, you aren’t seeing the full reporting data. Google now requires the Universal tag. If you upgrade your tag, you will see a return in reported organic traffic that is more in line with historical data.
Below, you’ll find a great example of an apparent traffic crash around Google Fred. Fortunately for this business, they were able to identify the problem and set a solution quickly. Since implementing the Universal Google Analytics tag, traffic has had a healthy return, higher than reporting average.
Imagine what might have happened to this business if they had not been paying attention to Google’s algorithm updates for several months.
Tip 2 – Audit your site for black hat SEO
Unsure if your employing black hat SEO tactics? Google has been cracking down on shady SEO tactics since 2006, and Google Fred is just a continuation on that core algorithm. In today’s SEO environment, having a few backlinks from sites with high domain authority is much better than boatloads of low-quality links. What has now been dubbed as “link farming” now does more harm than good.
As part of your audit, make sure you’ve removed as many low domain authority links as possible. Domain authority is a score of 1 to 100 based on how well a website will rank on search engines. Low domain authority is in the range of 1 to 30, and these links may be weighing your site down from its potential. If your website has been around for a while, it’s very likely that you’ve accumulated some unwanted low-quality links.
Can this happen to my website? Over the years, Google has taken action to delist a few Fortune 500 businesses with disastrous results.
Example 1: Google Panda – JC Penney
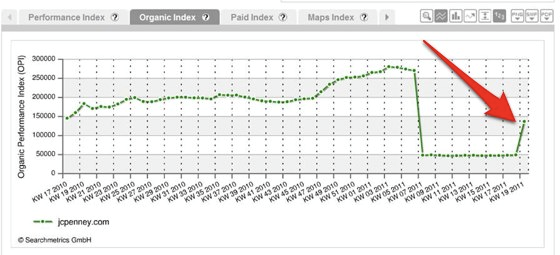
During the first iteration of Google Panda, JC Penney was delisted from Google for employing black hat SEO tactics. Google first caught the brand when JC Penney started ranking for suspicious terms Ranking for products they didn’t offer “bathroom tiles, online games, area rugs”.
What was JC Penney doing wrong?
The website was paying for backlinks from all sorts of spammy sites. The phrase “black dresses” and a Penney link were tacked to the bottom of a site called nuclear.engineeringaddict.com. “Evening dresses” appeared on a site called casino-focus.com. “Cocktail dresses” showed up on bulgariapropertyportal.com. ”Casual dresses” was on a site called elistofbanks.com. “Semi-formal dresses” was pasted, rather incongruously, on usclettermen.org. (Source: New York Times).
After discovering this, Google took immediate action in the Google Panda algorithm update, the first to delist websites based on their black hat SEO tactics. This was what happened: At 7 p.m. JC Penney was still the No. 1 result for “Samsonite carry on luggage.” Two hours later, it was at No. 71.
At 7 p.m. on Wednesday, Penney was No. 1 in searches for “living room furniture.” By 9 p.m., it had sunk to No. 68. In other words, one moment J.C. Penney was the most visible online destination for living room furniture in the country. The next moment, the Fortune 500 Company was essentially buried.
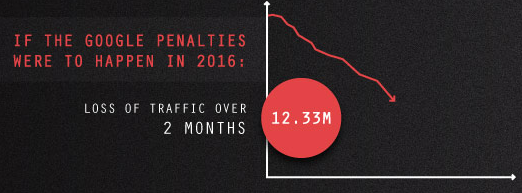
It took 90 days for the brand to recover rankings, that’s a lot of lost business! How much business was lost from this catastrophe?
JC Penney’s Keyword Rankings Plummet
Considering the ranking and search volume for their keywords, JC Penney lost an estimated 12.33 million visits in the 90 days the site was delisted.
Example 2: Google Penguin – The Home Depot
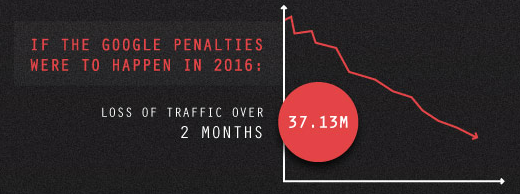
A short while after the JC Penney SEO disaster, Google penalized The Home Depot for asking over 2,000 services providers for backlinks, even suggesting that they hide the link. The Home Depot was hit by the Google Penguin update, focused on deranking sites with hidden backlinks.
Having a loose understanding of SEO, Home Depot took advantage of a Google loophole with hidden backlinks. They told their service providers to place a hidden link to the Home Depot home page, and by doing so your site will rank better.
For this action, Google delisted Home Depot from all search rankings for 2 months. The estimated traffic loss for Home Depot in these 2 months is 37.13 Million visitors.
Example 3: BMW
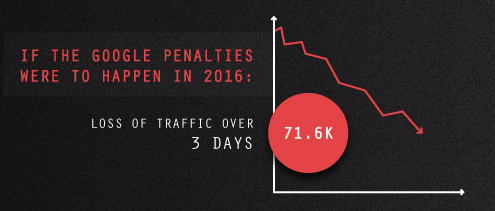
One of the earliest examples of a Google delisting was BMW in 2006. In these early days of Google, sites with obvious keywords suggested in their content were rewarded with higher ranked. However, Google realized this was not serving their users, with confusing content that didn’t ready naturally. BMW’s penalization came from keyword stuffing content for complete non-sense.
Their spammy web pages looked like:
These tactics did not pay off, as the main BMW website was completely removed from Google’s index for several days. An estimated 71.6K lost in traffic in this time frame. Keyword rankings and traffic returned when BMW removed these pages.
Tip 3 – Write “high-quality” content
With Google Fred, the search engine continues to fine-tune its algorithms for content. Google asserts that “high-quality” content will perform best on the search engines, but what does this mean exactly?
There are a few considerations for writing “high-quality” content that meets Google’s best practices. Here are the modern SEO rules.
Do’s:
- Original content: In calculating your website’s organic ranking, Google considers your content’s authoritativeness. Websites that highlight unique features of their business are more likely to rank than their competitors. This helps inform users about your business, which also helps with conversion rates. So, write content that is completely your own and site sources when necessary.
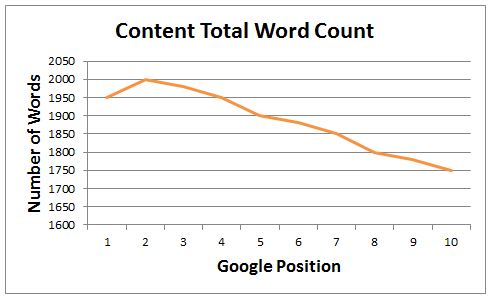
- Long-form content: Posts perform better if they’re long-form and easy to read. Posts that rank highest on Google are between 1,500 and 2,000 words. Even if you don’t write this length on every page, 500 words is the minimum to post on every page of your website.
Don’ts:
- Duplicate content: Earlier Google updates Hummingbird and RankBrain cracked down on duplicate content. You may have duplicate content if you have multiple URLs that have the same or similar content.
- Keyword stuffing: this practice will impact you negatively, so ease up on trying to fit your keyword into the copy as often as you can.
Tip 4 – Remove above-the-fold ads
Sistrix, an SEO data provider, describes sites affected as “…advertisement, outdated, thin and scraped content, as well as incomprehensible articles made up of 300 word ‘SEO texts’ pumped to the brim with main keyword mentions and void of any useful information or a sense of readability.” (Source: Sistrix.com)
Juan Gonzalez of Sistrix analyzed 300 sites throughout Germany, Spain, the UK, and the US which all lost SERP visibility around the time of the Fred update. Gonzalez reports that “nearly all losers were very advertisement heavy, especially banner ads, many of which were AdSense campaigns … Another thing that we often noticed was that those sites offered little or poor quality content, which had no value for the reader.” Fred is proving, once again, that content is king when it comes to high SEO value.
Below is a perfect example of a site hit by Google Fred. Notice the ads outlined in red bombard most of the above-the-fold content. The site doesn’t provide any lengthy content to redeem user experience, only a menu of link categories.
This site, Freewarefiles.com reportedly lost 75% of their keyword rankings during the Google Fred update. (Source: Sistrix.com)
Tip 5 – Inform yourself on latest Google algorithm shake-ups
How can you best prepare to protect your rankings? Read articles such as these!
Here are some key resources we follow daily to stay up-to-the minute on Google’s algorithm updates:
- Google Webmaster Central Blog
- Moz blog
- Search Engine Land
- Search Engine Watch
- Search Engine Journal
- Search Engine Roundtable
- AIS Media Blog
Google algorithm updates are frequent, and often shake-ups are reiterations of Google’s core algorithm. Because of this, older algorithm updates are still baked into the core algorithm, so if you’ve missed the boat on a past algorithm you may still be affected!
At AIS Media, we’ve audited many sites that seemed impacted by algorithm updates and never recovered. For example, sites that failed to comply with Google’s mobile-friendly update of 2015 are still experiencing traffic loss. Use Google Analytics as your tool to see the big picture, comparing your traffic year over year.
Conclusion
Overall, Google Fred hasn’t sprung anything on us that we didn’t at least suspect. It continues a lot of the trends we’ve already seen from Google updates. If you concentrate on these areas with your SEO in 2017, you should be in good shape. However, if you have questions, it may be a good idea to get in touch with professionals.
Need more customers?
AIS Media gets your business found when your ideal customers search online for what you offer. It’s what we’ve done for thousands of other businesses of all sizes since 1997. Get more details and check out the results others are getting from our SEO services.